This simulation shows how electricity consumption, solar production and battery storage affect two different houses over a day and a week.
You can adjust:
Location / climate zone
Season
House size and insulation
Heating type
Number of occupants
Solar system size (kWp)
Battery capacity for House B
Press Run Simulation to update the results.
A House (Orange) . . . . . B House (Green)
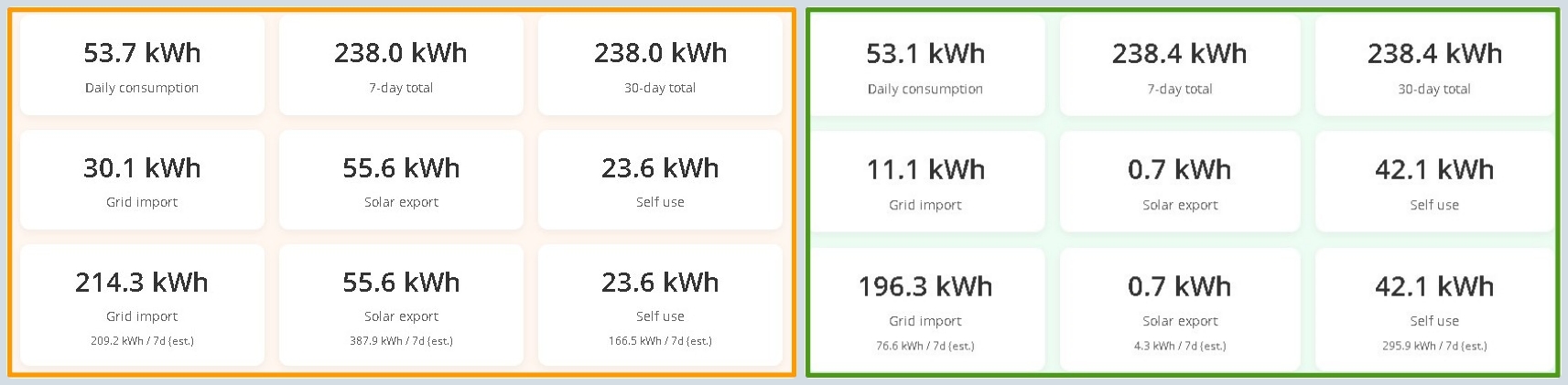
📊 Daily results (top row)
Daily consumption (kWh)
Total electricity used during the day.
7-day total / 30-day total
Accumulated estimates for weekly and monthly consumption.
⚡ Energy flows during the day (middle row)
Grid import (kWh)
Electricity purchased from the grid when solar production (and in House B, the battery) is not sufficient.
Solar export (kWh)
Solar electricity left over after covering on-site consumption and battery charging.
This is energy that would normally be exported to the grid.
👉 Note: this is not total solar production, only the surplus part.
Self use (kWh)
Solar electricity used on-site:
- House A: directly consumed
- House B: direct use plus energy discharged from the battery later
📅 Weekly totals (bottom row)
The bottom row shows cumulative weekly energy flows:
- Grid import = electricity bought during the week
- Solar export = surplus sent to the grid
- Self use = solar energy used on-site during the week
Smaller “/7d (est.)” values represent weekly estimates based on the current daily profile.
🔋 Why can Solar export be large?
With a large PV system and low daytime consumption, solar production can exceed what the house can use.
Without a battery or load shifting, much of the energy becomes surplus.
This is a realistic outcome for many solar installations.
Typical questions this simulation answers
This simulation lets you explore how solar panels, batteries and smart energy management change everyday electricity use. Try adjusting the settings and see how the results change.
⚡ How much electricity can solar panels produce at my location? Change the Location / Climate Zone, Season, and PV system size (kWp) to see how production varies between northern and southern Europe and between winter and summer. 🔋 How much grid electricity can I avoid with a battery? Increase Battery capacity for House B and compare: Grid import Self-use Solar export Notice how a battery shifts energy from daytime to evening and night. 🏠 What is the difference between House A and House B? House A represents a conventional solar home without a battery. House B shows an optimized system with storage and smarter energy usage. Run the simulation several times and compare the two. 🌞 What happens if I install “too many” solar panels? Increase the PV size and watch: Solar export rise Self-use level off Grid import shrink This helps estimate whether extra panels mainly benefit self-consumption or energy sales to the grid. 📆 How do seasons affect performance? Switch between Winter, Spring, Summer and Autumn. You will see how sunlight availability changes both daily production and weekly totals. 👨👩👧 How do household size and heating type matter? Try different: House sizes Number of occupants Heating systems These directly reshape the daily load curve and battery usefulness.Try it yourself: design your ideal solar home
Now it’s your turn.
Use the controls above to experiment with different system designs and see how they affect energy flows in real life. Try for example: increasing panel size and watching how solar export changes Adding battery capacity to reduce grid imports Switching seasons to compare winter vs summer performance Adjusting household size or heating type Comparing a conventional system (House A) with an optimized one (House B) There is no single perfect system. The goal is to find a balance between production, self-consumption, storage and cost that fits your home and lifestyle. If you would like a professional design based on your real site and consumption, our experts can prepare a tailored solar proposal for you.
